

REVIEW OF THE CASE
The opposer, Trane International INC., filed an opposition application against the trademark "TRANE and design" in Class 7 under the name of the opposed party Xia Bangbin, and received a favourable decision on the said trademark opposition application. After hearing, the China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) found that the registration of the opposed trademark infringed the prior copyright of the opposer, and decided, in accordance with the provisions of Article 32 and Article 35 of the Trademark Law, that the trademark shall not be registered.
CASE ANALYSIS
The opposed trademark designates the use of goods as Class 7 "mixers; household non-manual grinder, etc.”, the opposer cites the prior trademarks No.383898"![]() ", No.4562832""TRANE", No.898121"
", No.4562832""TRANE", No.898121" " and other trademarks, and the goods approved for use are Class 7"Refrigerant compressor; Condenser". The goods designated for use by the opposed trademark and the goods approved for use by the cited trademark do not belong to the similar goods on the "Similar Goods and Services Classification Table", and there are differences in functional use, sales channels, etc. Therefore, according to Article 30 of the Trademark Law, the possibility of success is not very optimistic.
" and other trademarks, and the goods approved for use are Class 7"Refrigerant compressor; Condenser". The goods designated for use by the opposed trademark and the goods approved for use by the cited trademark do not belong to the similar goods on the "Similar Goods and Services Classification Table", and there are differences in functional use, sales channels, etc. Therefore, according to Article 30 of the Trademark Law, the possibility of success is not very optimistic.
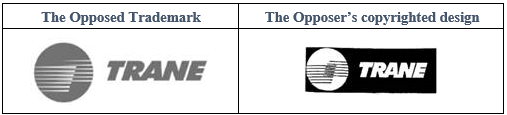
However, the opposed trademark and the opposer's copyrighted " " constitute substantial similarity, and the copyright's protection of the work is not limited by the class of goods, thus we have emphatically asserted that the opposed trademark is a facsimile of the opposer's prior copyright.
" constitute substantial similarity, and the copyright's protection of the work is not limited by the class of goods, thus we have emphatically asserted that the opposed trademark is a facsimile of the opposer's prior copyright.
The below is the comparison of the opposed trademark and prior copyrighted work of the opposer:
LEGAL GROUND
Criteria for the determination of copyright in the Guidelines for the Examination and Trial of Trademarks issued by the China Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA) in 2021:
3.2.2. Applicable Important Requirements
(1) Prior to the application for registration of the disputed trademark, another person has previously the copyright, and the copyright is within the term of protection.
The fact of prior copyright may be proved by the following evidence: evidence of prior public publication of the work, evidence of prior creation and completion of the work, certificate of registration of copyright, evidence of acquisition of prior copyright through inheritance or transfer, etc. The fact of prior copyright by the party concerned, as confirmed by an effective decision may be recognized in the absence of sufficient evidence to the contrary. A certificate of registration of a trademark or a certificate of registration of a copyright registered after the date of application for registration of the disputed trademark cannot, by itself, be used as evidence of the establishment of the prior copyright. A certificate of registration of a trademark or a certificate of registration of a copyright registered after the date on which the application for registration of the disputed trademark was filed cannot, on its own, be used to prove the existence of an earlier copyright.
(2) The disputed trademark is identical or substantially similar to someone else's copyrighted work.
(3) The applicant for the disputed trademark has had, or is likely to have, access to the copyrighted work of another person. If the applicant for registration of the disputed trademark can prove that the disputed trademark was independently created, this does not constitute an infringement of the prior copyright of others.
(4) The application for registration of the disputed trademark was made without the permission of the copyright owner.
Where the disputing trademark registrant claims that the application for registration of the disputed trademark has obtained the license of the copyright owner, he shall bear the burden of proving the license facts.
According to the above legal basis, when claiming prior copyright under the Trademark Law, the right holder must normally meet the following four elements of proof, and these four elements must be met simultaneously.
1. The trademark at issue in this case constitutes an artistic work under the Copyright Law
The law requires copyright works to meet two conditions: originality and an intellectual achievement that is aesthetically significant and capable of being reproduced in a tangible form. In this case, the opponent cited that the trademark " " is unique and original in design and constitutes a work of art.
" is unique and original in design and constitutes a work of art.
2. The right holder has a prior copyright in the work of art
In this case, we have provided information on the registration notice of the trademark No.898121" " in Class 11 and a large amount of evidence on the use of "
" in Class 11 and a large amount of evidence on the use of " ", including but not limited to: the trademark No. 898121"
", including but not limited to: the trademark No. 898121" " was awarded the "Certificate of Famous Trademark of Suzhou City" jointly issued by the Suzhou Trademark Association and the Suzhou Famous Trademark Recognition Committee on 2 February 2016, goods catalogues, the search report of National Library of China and sales evidence, etc, which show that the above evidence can prove that the " " artwork was publicly published in China before the date of filing of the opposed trademark application, and that the opposer is therefore entitled to prior copyrights in the artwork.
" was awarded the "Certificate of Famous Trademark of Suzhou City" jointly issued by the Suzhou Trademark Association and the Suzhou Famous Trademark Recognition Committee on 2 February 2016, goods catalogues, the search report of National Library of China and sales evidence, etc, which show that the above evidence can prove that the " " artwork was publicly published in China before the date of filing of the opposed trademark application, and that the opposer is therefore entitled to prior copyrights in the artwork.
3. Before the date of application for the trademark involved in the case, the applicant for the trademark involved in the case had the possibility of coming into contact with the work involved in the case
"Possible access to the work involved in the case" is generally proven by providing information on the prior public publication of the work, i.e. if the right holder can prove that the work has been publicly published, e.g. in newspapers, magazines, online media, exhibitions and fairs, it is presumed that the applicant for the disputed trademark has the possibility of access to the work involved in the case. In this case, the opposer " "has been publicly disclosed in advance by the prior application and preliminary examination announcement, while the opposer has also used and widely publicized in the market as its main commercial logo and has a certain degree of visibility. Therefore, it is presumed that the opposed party has the possibility of access to the opposer’s work.
"has been publicly disclosed in advance by the prior application and preliminary examination announcement, while the opposer has also used and widely publicized in the market as its main commercial logo and has a certain degree of visibility. Therefore, it is presumed that the opposed party has the possibility of access to the opposer’s work.
4. The trademark marks involved in the case are substantially similar to the works involved in the case
In this case, the opposed trademark and the opposer's copyrighted work are identical in terms of composition elements, design techniques and visual effects, and they can be considered to be substantially similar.
INSIGHTS FROM HANDLING CASES
When a certain logo design meets the requirements of the Copyright Law for works, copyright protection can be obtained without registration, and the protection of copyright works is not restricted by the category of goods. Copyright has its advantages in trademark objections and invalid cases, but the copyright registration certificate is not the natural basis for obtaining copyright protection, and other auxiliary evidence is needed. The key evidence lies in the evidence materials of the prior public publication of the work, the evidence materials of the prior creation of the work, and the evidence materials of obtaining the prior copyright through inheritance, transfer, etc.
 业务领域:
业务领域: 此案件代理人
此案件代理人
