

Recently, the opposition against the trademark No. 46683875 "design", which was acted by our law firm, has been ruled as the refusal of the registration by the Trademark Office of China National Intellectual Property Administration.
Profile of the Case
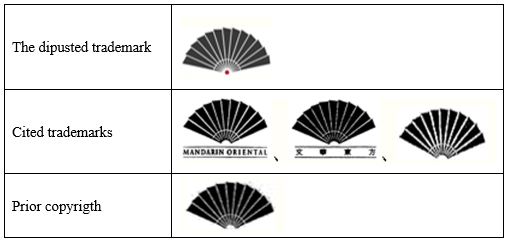
Dong Fang Mei Xue (Beijing)Culture Media Co., Ltd, the opposed party, has applied for the registration of the trademark ‘design’ with trademark number 46683875 (hereinafter referred to as the disputed trademark) on the Class 35 service ‘performing artist brokerage’, it has been published on No. 1757 Trademark Notice after the preliminary examination. Mandarin Oriental Hotel Group, the opposer, has cited prior trademarks on Class 42, i.e. “MANDARIN ORIENTAL and design’ with trademark number 771394, “文华东方及图”(Chinese in Pinyin Wen Hua Dong Fang and design) with trademark number 1467308, and the trademark “design”with trademark number 771393 (cited trademark from 1 to 3), as well as the prior copyright on the “FAN LOGO’, to file the opposition against the disputed trademark.
Mandarin Oriental Hotel Group
The Ruling of China National Intellectual Property Administration (CNIPA)
1. The designated service of the disputed trademark is Class 35 "Performing Artist Agent". The opposer’s prior cited trademarks 1 to 3 have been used under Class 42 (now Class 43) for services such as "hotel services; motor hotels; boarding houses". The trademark designated services of the parties are not similar services and therefore the trademarks of the parties do not constitute similar trademarks designated for use in the similar services.
2. The evidence provided by the opposer in this case can prove that the opposer obtained the Copyright Registration Certificate of "FAN LOGO" issued by the National Copyright Administration of China No. 00024537 on March 10, 2010. This time is earlier than the registration application date of the disputed trademark, so the opposer enjoys the prior copyright of the artwork.
3. There are slight differences in composition elements and visual effects between the disputed trademark’s design and the opposer's "FAN LOGO" artwork, which has formed a substantial similarity. The opposed party fails to provide evidence to prove that the disputed trademark is independently created. Therefore, the opposed party's application for registration of the disputed trademark infringes the prior copyright of the opposer.
As per Article 32 and 35 of the Trademark Law, the Trademark Office has ruled that No. 46683875 "design" trademark shall not be registered.
Analysis to the Case
Article 32 of the Trademark Law stipulates that "the application for trademark registration shall not harm the existing prior rights of others...". According to the Guide for Trademark Examination and Adjudication, the prior rights stipulated in this Article refer to other rights other than the trademark right that have been acquired before the date of registration of the contested trademark application, including the right of name, copyright, design patent, right of name, portrait, geographical indication and other legal prior rights and interests that should be protected.
In the above case, the designated service of the opposer’s cited trademark was not similar to the service of the disputed trademark. Therefore, the trademarks of both parties do not constitute similar trademarks used in similar services. However, the opposer successfully claimed the prior copyright of "FAN LOGO" by submitting the copyright registration certificate of "FAN LOGO" artwork, evidence of use, media reports and other evidential materials. In addition, the disputed trademark is substantially similar to the copyright, so the disputed trademark can be successfully destroyed, furthermore, to ensure the opposer’s legitimate rights and interests.
China adopts the principle of "voluntary registration" for copyright registration, doesn't force registration of works, but a Copyright Registration certificate with the registration date earlier than the application date of the disputed trademark, in the absence of evidence to the contrary, the copyright registration certificate can prove that the prior owner enjoys the prior copyright to this work of fine art.
For the case where the copyright registration date is later than the application date of the disputed trademark, the prior right holder needs to properly keep the design manuscript, original and other evidence materials that can effectively prove the creation process, or release the evidence of the art work in the open field. When the relevant evidence verifies each other and forms a relatively complete evidence chain, it may claim that the party has a prior copyright in the trademark.
In short, the copyright registration certificate, as the direct evidence to prove the ownership of copyright, plays an important role in the opposition and invalidation cases because it is not restricted by the classes of goods and services as the prior right. Therefore, it is suggested that the right holder register the copyright protection of the relevant rights. At the same time, the copyright owner should also keep the evidence of the completion of the creation, such as the manuscript of the creation, and the evidence of the first public publication and use.
Janlea intellectual property rights has a professional team of copyright, can provide efficient and high-quality services for your copyright protection.
 业务领域:
业务领域: 此案件代理人
此案件代理人
